For the latest research outputs of the project check out our:
Overview
Knowledge graphs (KGs) are a flexible knowledge representation paradigm intended to facilitate the processing of knowledge for both humans and machines at Web scale. They are widely regarded as a key enabler for a number of increasingly popular technologies , including Web search, question answering, personal assistants, and (explainable) AI across most sectors including finance, Industry 4.0, personalised medicine, legislation, economics and more.
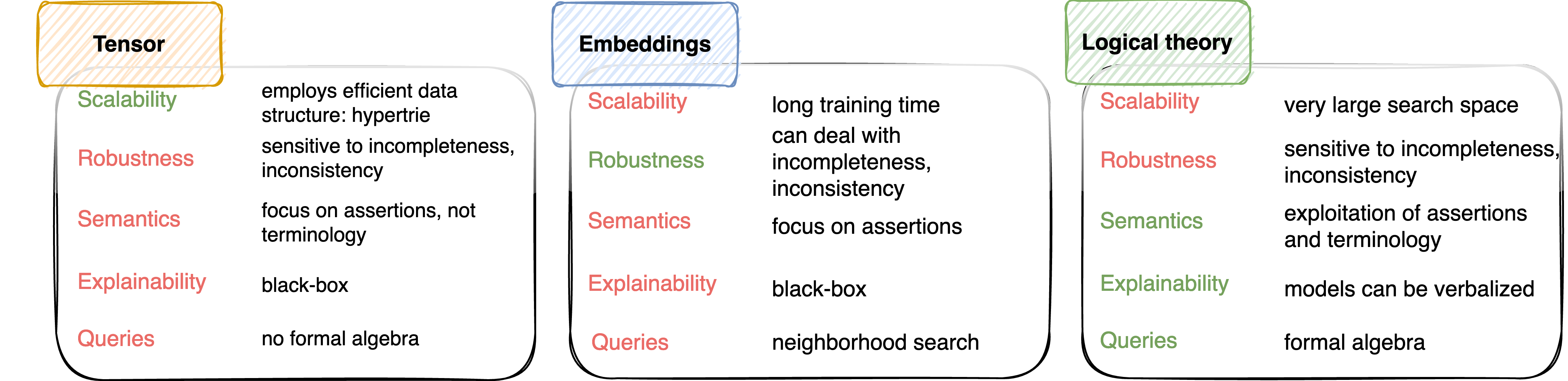
However, current AI and especially machine learning (ML) approaches for KGs (e.g., class expression learning (CEL), inductive logic programming (ILP), graph neural networks, graph convolutional networks, graph attention networks, etc.)
- fail to scale to large graphs with billions of edges,
- are bound to consistency in particular formalisms (e.g., description logics, Horn logics),
- fail to exploit the semantics modelled into the KGs, or
- rely on a one-shot explanation paradigm if they are at all explainable.
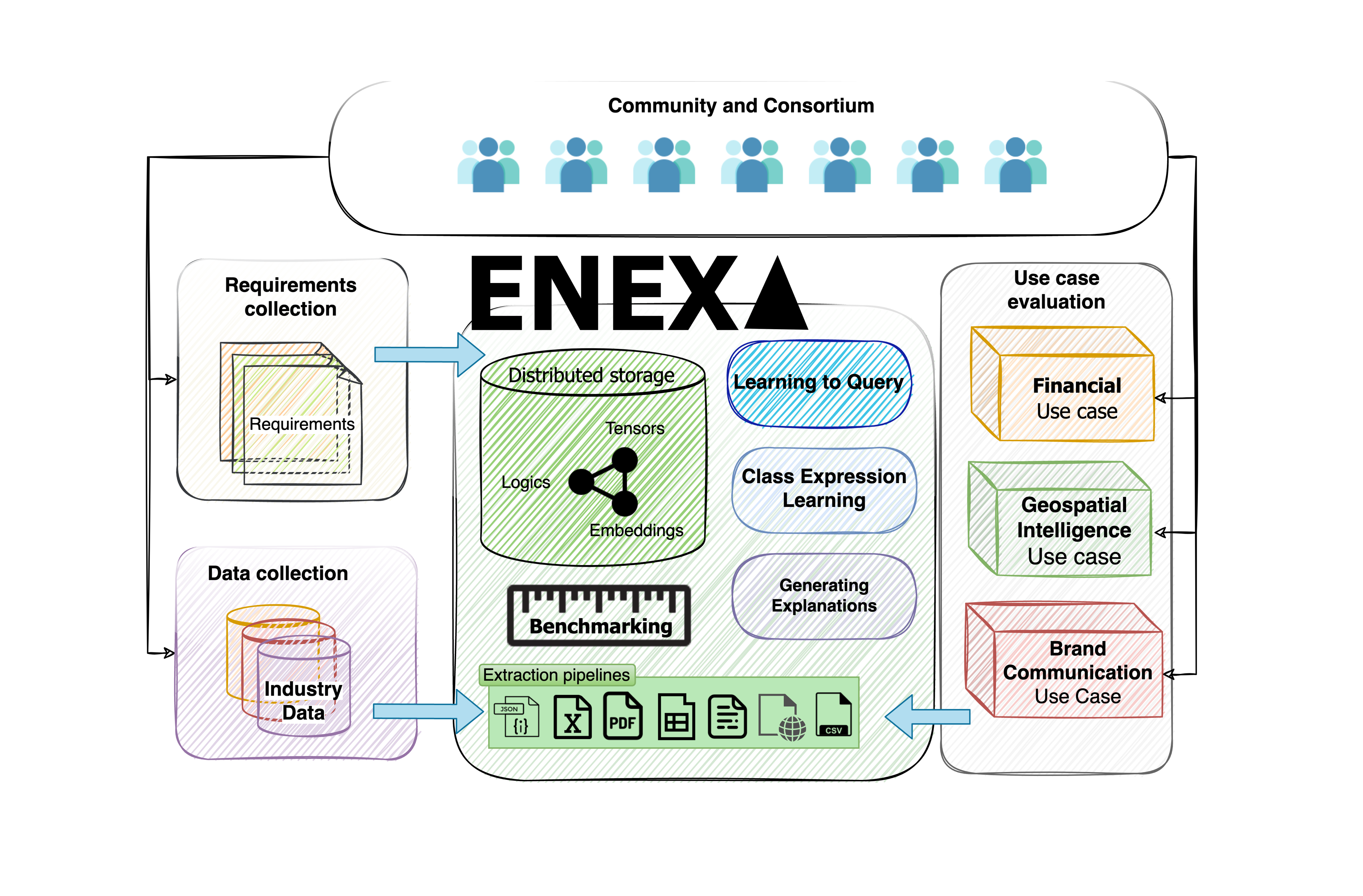
The core objective of ENEXA is to address the challenge of developing explainable machine learning (ML) approaches for real-world knowledge graphs (KGs) with a focus on human-centered explanations. To achieve this goal, ENEXA will develop novel hybrid ML approaches that can exploit multiple representations of knowledge graphs concurrently. The approaches developed in the project will tackle real-life runtime requirements and make explainable machine learning amenable to Web-scale applications. By providing a concrete implementation of the novel concept of explanation co-construction, ENEXA will pioneer the implementation of explanation models grounded in sociology and psychology in hybrid machine learning to provide human-centered explanations for machine learning models.
To tackle this objective, the project takes advantage of the strengths of the various representations of knowledge graphs, which we term the representation trichotomy.